
Blood plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation.Body Fluid Compartments volume from plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. It is the external environment for the cells. Calculated by subtracting the extracellular fluid Extracellular fluid The fluid of the body that is outside of cells.Accounts for ⅔ of the extracellular fluid Extracellular fluid The fluid of the body that is outside of cells.Interstitial fluid Interstitial fluid Body Fluid Compartments :.It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Radioactive sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals.Mannitol is also commonly used as a research tool in cell biological studies, usually to control osmolarity. It can be used to treat oliguria associated with kidney failure or other manifestations of inadequate renal function and has been used for determination of glomerular filtration rate. It has little significant energy value as it is largely eliminated from the body before any metabolism can take place. Mannitol Mannitol A diuretic and renal diagnostic aid related to sorbitol.It has been used in physiologic investigation for determination of the rate of glomerular function. Since it is hydrolyzable to fructose, it is classified as a fructosan. Inulin Inulin A starch found in the tubers and roots of many plants.Accounts for ⅓ of total body water Total body water Body Fluid Compartments.Body Fluid Compartments volumeĮxtracellular fluid Extracellular fluid The fluid of the body that is outside of cells. Calculated by subtracting the total body water Total body water Body Fluid Compartments from extracellular fluid Extracellular fluid The fluid of the body that is outside of cells.The total volume contained by all cells in the body.Accounts for ⅔ of total body water Total body water Body Fluid Compartments.Symptoms vary depending on location of the edema.īody Fluid Compartments Intracellular fluid Intracellular fluid The fluid inside cells. Edema can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity).

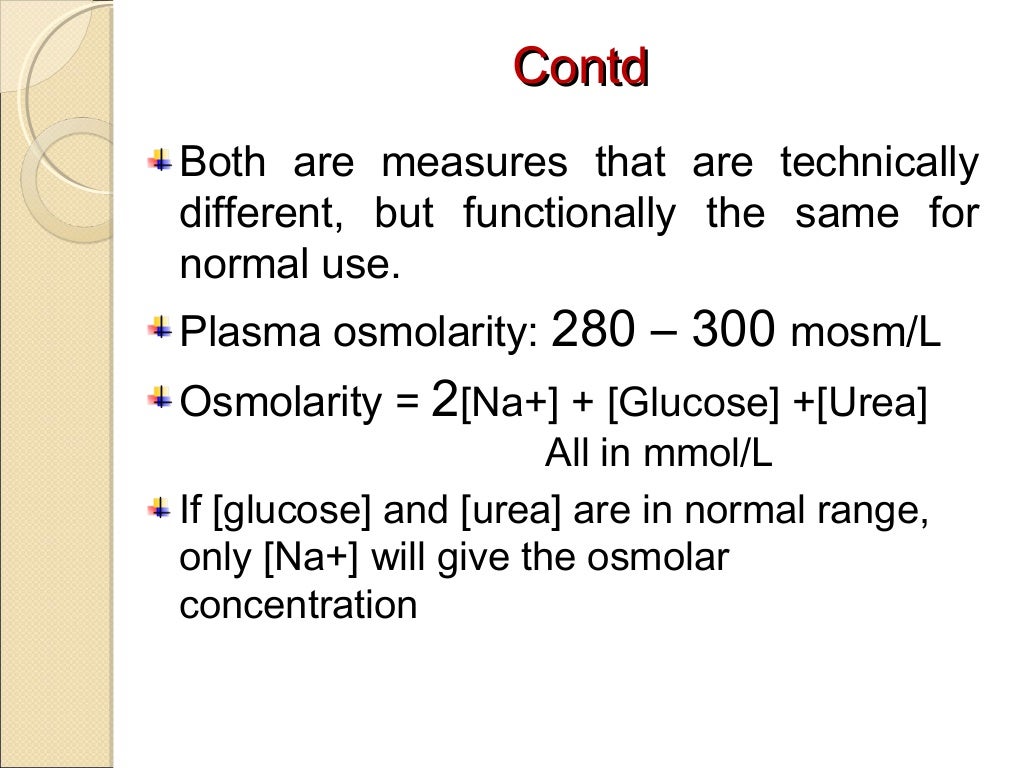
Hypernatremia, and Starling forces Starling Forces Capillaries: Histology. Osmolality is expressed in terms of osmoles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
Body Fluid Compartments, fluid osmolarity Osmolarity The concentration of osmotically active particles in solution expressed in terms of osmoles of solute per liter of solution. Intracellular fluid is present inside the cells and makes up two-thirds of the total body water. Extracellular fluid is present outside the cells and makes up two-thirds of the total body water. Fluid dynamics in the body depend on body fluid compartments Body fluid compartments The adult human body is made up of 60% water and is divided into extracellular and intracellular fluid compartments. Edema is a sign observed in several medical conditions.
BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS USMLE PRO

This means ~2.5L of "blood" is the "intracellular fluid of RBCs".



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
